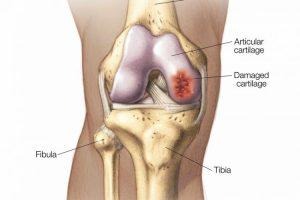
What is Cartilage repair/restoration?

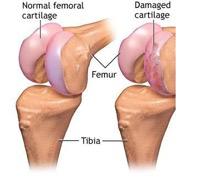
Repair and restoration of cartilage is a procedure for joints with damaged, but otherwise good, cartilage. For patients with cartilage damage or deterioration, treatment is recommended.
Knee Cartilage Repair – Special instruments can be used by a surgeon to remove the broken cartilage and smoother the leftover cartilage surface. This contouring lowers joint friction which in turn can lower knee pain, regain knee function and slow down potential degeneration of cartilage.
Knee Cartilage Regeneration – The ability of cartilage tissue to repair itself is severely reduced because it has no blood vessels, and bleeding is required for healing. By making small cuts or abrasions in the bone of the injured cartilage, a surgeon can stimulate new cartilage growth. The damaged bone blood will contribute to new cell growth in cartilage.
Symptoms of Cartilage restoration?
- Stiffness
- The limb will not move freely
- Joint pain
- Swelling
- Grinding sensation
Evaluations for Cartilage restoration
- Physical examination
- MRI
- X-rays
- Arthroscopy
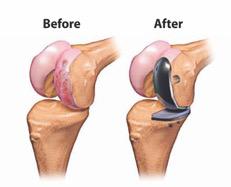
Treatment for Cartilage repair/restoration
The restoration of articular cartilage is done arthroscopically in most procedures.
For cartilage reconstruction, the common procedures are:
- Microfracture – The microfracture objective is to encourage the development of fresh articular cartilage by generating a fresh supply of blood. To create multiple holes in the joint surface, a sharp instrument is used. The holes, called subchondral bone, are made in the bone under the cartilage. New blood supply to the joined surface can lead to new cells that are to form the new cartilage. This action leads to a healing effect.
- Drilling – Drilling stimulates the development of good cartilage, such as microfracture. In the subchondral bone, multiple holes are created with a surgical drill or wire through the injured area. A healing reaction is created by penetrating the subchondral bone.
- Abrasion Arthroplasty – Abrasion arthroplasty is equivalent to drilling. High-speed burrs are used to separate the damaged cartilage and achieve the subchondral bone rather than drills or wires.
- Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) – Arthroscopically, a surgeon removes, from the knee, a small portion of the cartilage. The tissue is then sent to a laboratory for cultivation. A second surgery is needed in order to implant the lab-grown cells at the damaged cartilage site.
- Osteochondral Allografts – The damaged cartilage is repaired by a donor’s bone.
- Osteochondral Autograft – A surgeon removes and transplants a bone plug with cartilage on the healthy joint region.
Estimated Costs:
The cost of Investigations would generally range between USD 400 and USD 600
The cost of surgery would generally be as below:
| Economy Ward | USD 2800 |
| Twin Sharing Room | USD 3400 |
| Private room | USD 4000 |
In the case of Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation, the cost may go up to USD 11000 including the cost of the implant.