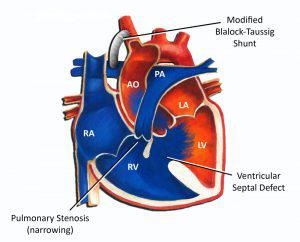
· A palliative (temporary) treatment used to improve the blood flow to the lungs in conditions such as Pulmonary Atresia, severe Pulmonary Stenosis, Tricuspid Atresia, and severe Fallot’s Tetralogy, until such time as the defect can be repaired.
· This is usually a closed heart procedure which is carried out through an incision through the ribcage on the right or left of the child’s back. The shunt (a small tube of synthetic material) is attached to one of the sections of the blood vessel to the arm and to the pulmonary artery making a direct connection between the aorta and the lungs (mimicking the ductus arteriosus).
· This allows more blood to flow to the lungs and improves the oxygen saturation levels (SAT’s) relieving severe blueness (cyanosis) that the child may be experiencing.
· A staged operation may be done depending on the baby’s symptoms and oxygen saturations. This usually begins with a BT Shunt, than a complete repair at about six months which involves removing the pulmonary obstruction, closing the ventricular septal defect with a patch, and sometimes enlarging the pulmonary artery if needed.
· For that baby has to be about year old and it has to be weight 11kg