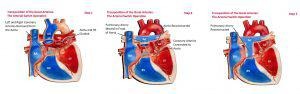
Arterial switch operation surgery is a surgical procedure to correct the Transposition of the great arteries (TGA).
Transposition of the great arteries (TGA) is the most common cyanotic congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates. The hallmark of transposition of the great arteries is ventriculoarterial discordance, in which the aorta arises from the morphologic right ventricle and the pulmonary artery arises from the morphologic left ventricle. The result is that blood containing oxygen from the lungs is pumped back into the lungs, while blood that lacks oxygen, which is necessary to nourish the body, is pumped throughout the body.
During the operation, the pulmonary artery and the aorta are “switched” back to their normal positions and the coronary arteries are attached to the new aorta in the correct positions. The atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect, if present, are closed with patches and the patent ductus arteriosus is tied off. This is an open-heart procedure that is usually done within the first few weeks of life.