
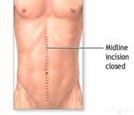
The appendix sits at the junction of the small intestine and large intestine. It’s a thin tube about four inches long. Normally, the appendix sits in the lower right abdomen.
Appendicitis is a condition in which your appendix becomes inflamed and fills with pus. Your appendix is a finger-shaped pouch that projects out from your colon on the lower right side of your abdomen. This small structure has no known essential purpose, but that doesn’t mean it can’t cause problems.
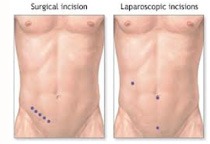
Laparoscopic Surgery:The laparoscopic (minimally invasive) surgical technique involves making several tiny cuts in the abdomen and inserting a miniature camera and surgical instruments. As many as three or four incisions are made. The surgeon then removes the appendix with the instruments, so there is usually no need to make a large incision in the abdomen. The camera projects a magnified image of the area onto a television monitor which helps guide the surgeons as they remove the appendix. Laparoscopic surgery also requires general anesthesia and it can last up to two hours.




Cancer Treatment in India, VSD Closure (Ventricular Septal Defect), ASD Closure Surgery (Atrial Septal Defect), Heart hole closure surgery in india, Brain Tumour Surgery in India, Craniotomy Surgery for Treatment of Brain Tumour in India, Brain Stem Glioma Treatment in India, Deep Brain Stimulation surgery in india , Best Spine Surgery In India , Cervical Spine Disorders Surgery and Treatment in india , epilepsy surgery in india , Heart Surgery in india , Best open heart surgery hospital in India , All about Spine Surgery, Types of Back Surgery , Top Doctors In India , Best Hospitals in India , Bhavin Desai cardiac surgeon, Best kidney transplant doctor in IndiaBest hospital for limb lengthening surgery in India, Best hospital for neurosurgery in India, Best hospital for bypass surgery in India, Narayana Hrudayalaya online appointment, Best orthopedic hospital in Bangalore, Best open heart surgery hospital in India, Best bypass surgeon in India, best spine surgery hospital in India, Artemis hospital Gurgaon, KD hospital medical appointment
Limb lengthening surgery cost in India, DSA test, Diabetes treatment in India