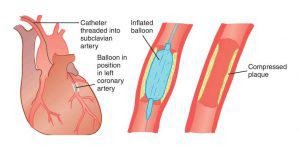
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) is a minimally invasive procedure to open up blocked coronary arteries, allowing blood to circulate unobstructed to the heart muscle.

ANGIOPLASTY TREATMENT IN INDIA
Angioplasty is an invasive procedure to open narrowed or blocked arteries caused by the deposits of plaque and it is also used restore blood flow through the artery. Doctors also refer to angioplasty as percutaneous coronary intervention, or PCI. Angioplasty is recommended by the cardiologist to the patient to remove the sticky material called plaque. In Angioplasty, it uses a tiny balloon catheter that is inserted in a blocked blood vessel to help widen it and improve blood flow to the heart. Angioplasty is a conventional treatment for coronary heart disease (CHD) and heart attacks (acute coronary syndrome).
TYPES OF ANGIOPLASTY:
There are two main types of angioplasty
- Balloon Angioplasty: This involves using the pressure of an inflating balloon to clear plaque that is blocking the artery. This process is required when doctors are unbale to place a stent in the required position.
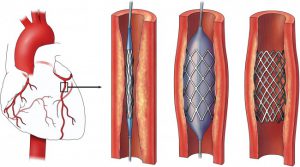
- Stent Placement: It is the placement in the artery, which involves a tube or stent made from wire mesh. Stents help to prevent an artery narrowing again after angioplasty. Stents are made of bare metal or have a coating of medication.
WHY THE PROCEDURE IS PERFORMED-
Arteries can become narrowed or blocked by deposits called plaque. Plaque is made up of fat and cholesterol that builds up on the inside of artery walls. This condition is called hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis).
Angioplasty may be used to treat:
- Blockage in a coronary artery during or after a heart attack
- Blockage or narrowing of one or more coronary arteries that may lead to poor heart function (heart failure)
- Narrowings that reduce blood flow and cause persistent chest pain (angina) that medicines do not control
Not every blockage can be treated with angioplasty. Some people who have several blockages or blockages in certain locations may need coronary bypass surgery.
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION ANGIOPLASTY:
- ECG: Electrocardiogram is a test to detect and record heart’s electrical activity and help to locate the heart problem.
- Stress Test: Basically, exercise test to make heart work hard.
- Echocardiography: uses sound waves to create a moving picture of heart.
- Coronary Angiography: uses dyes and x-rays to show the inside view of the arteries.
- Laboratory Test: Includes number of blood tests to diagnose and monitor treatment for heart disease.
PROCEDURE OF ANGIOPLASTY:
- 1st Step: Before beginning angioplasty, a healthcare professional will clean and numb the area where the catheter enters the body, usually the groin but sometimes the wrist.
- 2nd Step: Next, a doctor inserts the catheter into the artery and directs it towards the coronary artery, watching its progress on an X-ray feed.
- 3rd Step: Once the catheter is in position, the doctor injects a contrast dye through the artery, which helps identify blockages around the heart. Once they locate the blockages, the doctor inserts a second catheter and a guidewire, usually with a balloon at the tip.
- 4th Step: When the second catheter is in position, the doctor inflates the balloon, which pushes the plaque buildup away and opens the artery. The surgeon may insert a stent to keep the artery propped open.
RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH ANGIOPLASTY:
Angioplasty is generally safe, the procedure still carries some risks. The most common angioplasty risks include:
- Damage to blood vessels, Kidneys or arteries.
- An allergic to the dye.
- Chest pain.
- Blood clot.
- Heart attack.
- A tear or damage to artery or major blood vessel.
RECOVERY AFTER ANGIOPLASTY:
- After angioplasty, the cardiologist removes the catheters and bandages.
- Soreness, bruising, and possibly bleeding is common around the area where catheters entered the body.
- Patient will recover in the hospital within few hours or overnight before going home.
- Patient must not drive as they may still have sedative medications in their system.
- Patient have restrictions on lifting for about the week.
- Patient can return to work within a week but after consulting their surgeon.
- The key aspect of the treatment is the follow-up visit after angioplasty.
The doctor will review the patient’s recovery, adjust medications as they need, and develop an ongoing treatment plan for their cardiovascular health.