What is Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery?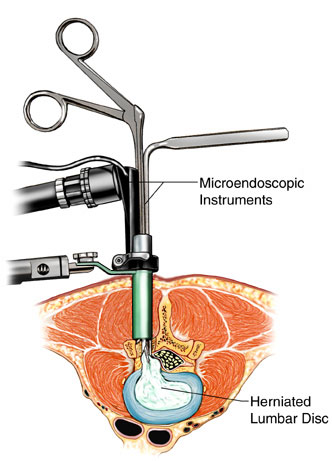
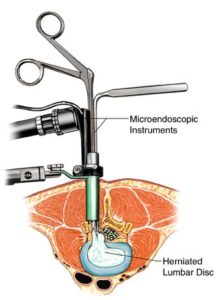
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery is a spinal bone surgery. Smaller incisions are used in this form of surgery. This causes less damage to adjacent tissue and muscles. After surgery, it can lead to less pain and more quick recovery. Open surgery is called the generic form of spinal surgery. It is performed by a long back incision. Muscles and soft tissue should be moved away around the spine. Tissue must be removed in some cases. The doctor makes a smaller incision during MISS, and then inserts a device called a tubular retractor. A stiff, tube-shaped instrument forms a tunnel to the spinal issue region and pulls muscle and soft tissue around it softly. The surgeon can then use tiny instruments to operate on the spine via the tunnel. The doctor uses a microscope to see X-ray images of the spine in real time.
What are the symptoms leading to doctor’s recommending – Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery?
- Pain
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness
- Stiffness
- Muscle spasms
- Tingling
Evaluations for Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
- X-rays
- CT scan
- MRI
- Electromyograms
- Myelogram
Treatment for Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
MISS fusions and processes for decompression are carried out in numerous ways. A tubular retractor is the most common form. A tiny incision is created during the treatment and the tubular retractor is inserted into the spinal column via the skin and soft tissue. This forms a tunnel to the small area of the spine. The tubular retractor keeps the muscles open and remains in place during the entire procedure. With tiny tools, the doctor can reach the spine via the middle of the tubular retractor. Any bone or disk material taken passes via the retractor and any fusion-related devices, such as screws or rods, are placed through the retractor. Some surgeries involve more than one or more incisions. The surgeon is guided by fluoroscopy to see where to position the incision and insert the retractor. This technique shows pictures of the patient’s spine in real time on a screen during the whole procedure. Typically, the surgeon uses a microscope to view the essential structures of the spine. The tubular retractor is removed at the end of the surgery and the muscles come back to their original position, thus reducing muscle damage, which is most common in open surgery.
Estimated Costs
| Hospital | City | Cost of Investigations | Cost of Surgery for 1 Level |
| Artemis Hospital | Gurugram | USD 400 – USD 500 | USD 6400 |
| Jaypee Hospital | Greater Noida | USD 400 – USD 500 | USD 6800 |
| BLK Super Speciality Hospital | New Delhi | USD 400 – USD 500 | USD 7200 |
| W Pratiksha Hospital | Gurugram | USD 400 – USD 500 | USD 6000 |
| Apollo Hospital | Chennai | USD 400 – USD 500 | USD 7200 |
| Global Hospitals | Bengaluru | USD 400 – USD 500 | USD 6400 |
| Sharda University Hospital | Greater Noida | USD 400 – USD 500 | USD 5900 |